uwsgi代码学习#
概况#
https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
unbit/uwsgi
uwsgi项目的目标是开发全栈web服务。
主要是一个wsgi服务器,并包含了各种相关功能。实际使用中有茫茫多的选项。
囊括的知识点可以说是巨多。
包括linux进程/线程/协程相关,网络相关,python的c接口相关,等等。
很多功能做成了plugin的形式。
代码不算庞大,花一定时间是可以看个大概的。
可以学到uwsgi的各种功能和用法,更好地干活。
可以学到很多linux/c/python/工程知识。
下面把web服务相关的流程大概过一遍。
只看主要流程,忽略细节。
wsgi
https://peps.python.org/pep-3333/
https://wsgi.readthedocs.io/en/latest/learn.html
python
https://docs.python.org/3/c-api/
https://docs.python.org/3/extending/embedding.html
pthread
http://lemuria.cis.vtc.edu/~pchapin/TutorialPthread/pthread-Tutorial.pdf
https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E53394_01/html/E54803/tlib-1.html
https://www.ibm.com/docs/en/i/7.2?topic=category-pthread-apis
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/pthreads.7.html
https://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/academic/class/15492-f07/www/pthreads.html
https://pubs.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/9699919799/basedefs/pthread.h.html
环境和配置#
linux
uwsgi 2.0.21
python 3.1x
实际环境中的主要组件
nginx
uwsgi
gevent/libev
flask
以下述配置看代码
[uwsgi]
# python插件参数
module = main
callable = main_app
# gevent插件参数
gevent = 256
gevent-early-monkey-patch = 1
# uwsgi的参数
chdir = /xxx/xxx/projects/xxx
touch-reload = /xxx/xxx/projects/xxx/main.py
socket = 0.0.0.0:10000
#location of log files
logto = /xxx/xxx/log/xxx.log
log-maxsize = 10000000 # 10m
single-interpreter = true
#run on subdir. really hard to find the solution
mount = /api/=main.py
manage-script-name = True
processes = 4
listen = 1024
reload-mercy = 20
worker-reload-mercy = 20
stats=0.0.0.0:10010
stats-http = True
# 其他应用
attach-daemon = python /xxx/xxx/projects/xxx/deploy/uwsgi_monitor.py
看代码时打开宏
UWSGI_EVENT_USE_EPOLL
PYTHREE
__linux__
UWSGI_LOCK_USE_MUTEX
代码分析#
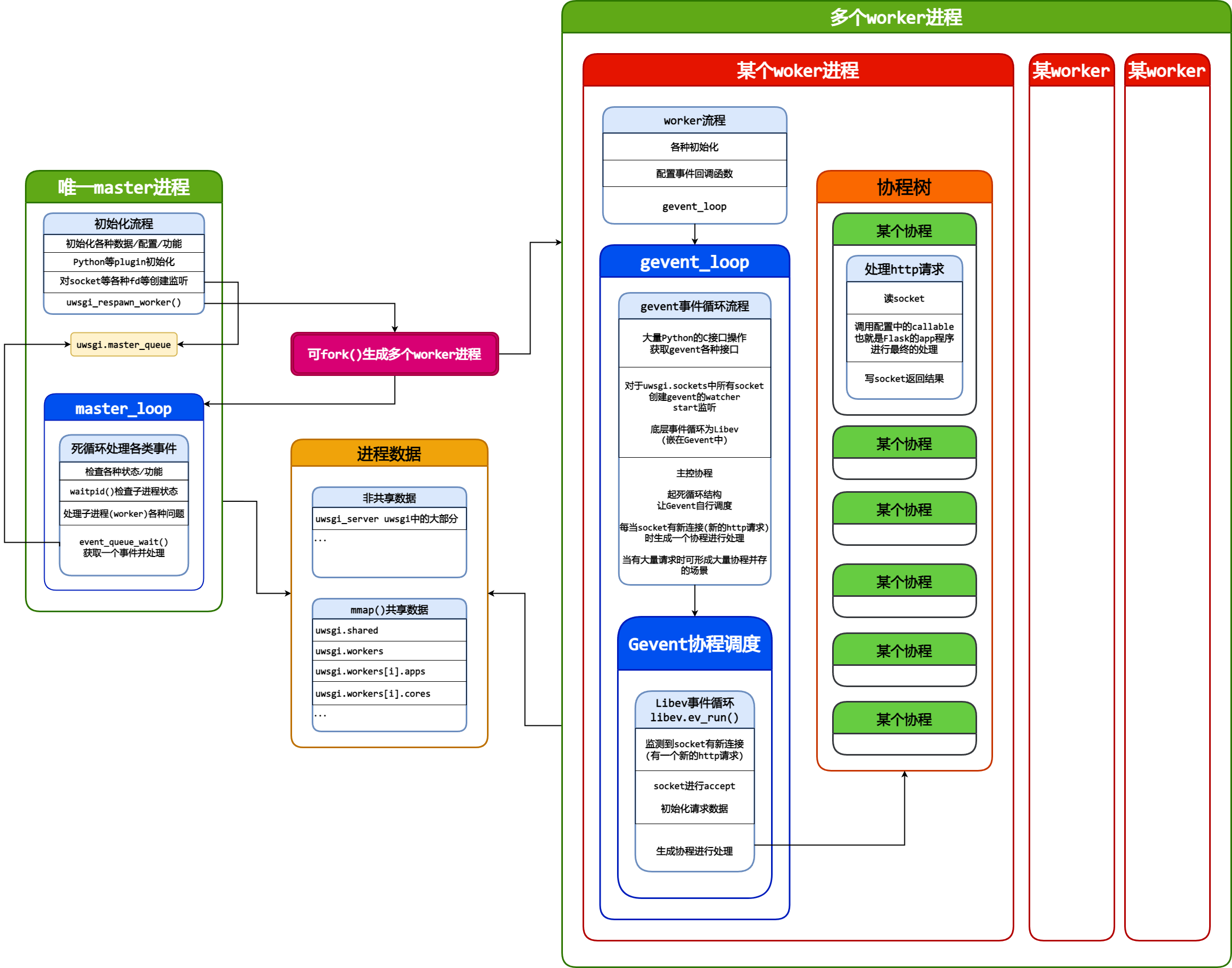
整体结构主要是一个master进程,和多个worker进程。
几乎所有数据都在struct uwsgi_server,超大的结构体。
其中一些数据用mmap分配内存,可在进程间方便地共享。
master负责管理worker的状态。
worker负责接受大量请求并生成协程进行处理。
主要结构体#
// plugin是非常重要的内容。这个软件许多功能都是做成plugin的形式。
// plugin分为request plugin和generic plugin
// 主要看python和gevent两个plugin
/*
uwsgi --plugin-list 可列出加载的plugin
--show-config 可列出最终的配置
--logger-list
--cheaper-algo-list
--router-list
--loop-list
--imperial-monitor-list
--clock-list
--alarms-list
一起打印出来看看有个大概映像
uwsgi --plugin-list --show-config --logger-list --cheaper-algo-list --router-list --loop-list --imperial-monitor-list --clock-list --alarms-list
*/
// 我是用pip安装的uwsgi,列出来有四五十个plugin。
// 找了一圈没找到加载这些plugin的代码。估计是pip的版本编译时内置的,暂不纠结。
// 见 ULEP宏 UWSGI_LOAD_EMBEDDED_PLUGINS UWSGI_EMBED_PLUGINS
// 见buildconf文件夹
struct uwsgi_plugin {
const char *name; // 名字
// 各种回调
int (*init) (void);
// ...
}
// 一个app。例如一个flask项目。
struct uwsgi_app {
void *callable; // wsgi的callable名字
void **args; // 参数
void **environ; // 参数/环境
// 处理请求的回调
void *(*request_subhandler) (struct wsgi_request *, struct uwsgi_app *);
int (*response_subhandler) (struct wsgi_request *);
// ...
}
// 一个请求相关的数据
struct wsgi_request {
int fd;
int app_id;
int async_id; // 根据core数量从0开始编号。
void *async_args; // 参数
void *async_environ; // 参数/环境
// ...
}
// uwsgi_core用来承载一个请求
struct uwsgi_core {
int in_request; // 是否正在处理请求
struct wsgi_request req;
// ...
}
struct uwsgi_worker {
int id;
pid_t pid;
uint64_t status;
int manage_next_request;
int apps_cnt;
struct uwsgi_app *apps;
struct uwsgi_core *cores;
// ...
}
// mule功能
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Mules.html
struct uwsgi_mule {
int id;
pid_t pid;
}
// 某些plugin会用到mule,
// daemon是master另外维护的进程
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/AttachingDaemons.html
// attach-daemon参数添加daemon程序
struct uwsgi_daemon {
char *command; // 要执行的命令
}
// uwsgi大状态
struct uwsgi_instance_status {
int gracefully_reloading;
int brutally_reloading;
int gracefully_destroying;
int brutally_destroying;
int chain_reloading;
int workers_reloading;
int is_cheap; // spawn workers only after the first request
int is_cleaning;
int dying_for_need_app;
};
// mmap分配各种共享数据
struct uwsgi_shared {
}
struct uwsgi_socket {
// 各种socket基本数据
int fd;
int family;
// https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/epoll.7.html
// https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Epoll
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9162712/what-is-the-purpose-of-epolls-edge-triggered-option
// https://lwn.net/Articles/864947/
int edge_trigger; // epoll的trigger模式。是个大课题。可默认为level trigger
// 简单来说。编程模型不一样。(我没有系统地写过这种事件处理程序。可能理解有误)
// edge trigger是告诉你状态发生变化了,可读写了。
// 只通知一次,此时你要记住这次通知,尽可能多读/写,直到读写接口返回EAGAIN等。然后等待下次触发。
// level trigger是告知目前的状态是可读写数据。
// 我们可以更随意地安排读写,即使一次读写不完,过会再poll,还是能继续读写。
// edge trigger的区别在于,如果一次不读写完,你再poll,可能就poll不到事件,因为此时状态可能没有改变。
// 实际的例子。监听socket,有新客户端连上来,走py_uwsgi_gevent_main。
// 假设此时有3个客户端连上来。如果level trigger,可以accept一个就退出,再poll,还是能poll到后面的客户端。
// 而如果是edge trigger,就得不断尝试accept,直到确实没有新客户端。
// 如果此时accept第1个就退出,那么再poll就poll不到剩下的2个客户端,直到又有第4个客户端连上来才能再次poll到。那么就造成了第2/3个卡住得不到accept。
// 各种基本操作的配置。比如accept时用什么函数
int (*proto_accept) (struct wsgi_request *, int);
int (*proto) (struct wsgi_request *);
// ...
}
// uwsgi_server包含服务器各种主要数据,有将近1000个member。
struct uwsgi_server {
char hostname[256];
int hostname_len;
int need_app; // need-app参数。必须要有app,如果没有,kill_them_all()。
// 存一堆协议处理函数
int (*proto_hooks[UWSGI_PROTO_MAX_CHECK]) (struct wsgi_request *, char *, char *, uint16_t);
int numproc; // worker进程数量。processes或workers参数可设置。我们设置processes=4。
int async; // async参数或gevent参数。我们设置gevent=256
int threads; // threads参数。我们不设置,默认为1。
int cores; // = uwsgi.async或uwsgi.threads。gevent=256所以cores=256
struct uwsgi_instance_status status;
struct uwsgi_plugin *p[256]; // request plugin
struct uwsgi_plugin *gp[MAX_GENERIC_PLUGINS]; // generic plugin
int gp_cnt;
struct uwsgi_worker *workers;
pid_t mypid; // 我的pid
int mywid; // 我的worker id
char *loop; // 指定loop
// mule
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Mules.html
int muleid;
int mules_cnt;
int farms_cnt;
struct uwsgi_mule *mules;
struct uwsgi_farm *farms;
int listen_queue; // listen参数。set the socket listen queue size
int manage_next_request; // 指示worker是否还要处理下个请求。用在启动和停止时。
struct uwsgi_daemon *daemons;
int master_process; // 貌似。是否起主控进程。如果配置的选项有UWSGI_OPT_MASTER,就会打开。较多选项都是如此。
int master_queue; // io消息系统实例的fd。比如epoll。
char *zerg_server; // zerg模式
char *stats; // states服务。用于外部查询server状态
struct uwsgi_shared *shared; // mmap共享内存
struct uwsgi_protocol *protocols;
struct uwsgi_socket *sockets;
struct uwsgi_socket *shared_sockets;
// ...
}
// python plugin的主数据
struct uwsgi_python {
char *callable; // callable参数
// ...
}
// gevent plugin数据
struct uwsgi_gevent {
PyObject **watchers;
// ...
}
master#
uwsgi_server uwsgi; // server主数据
main
uwsgi_setup
signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_DFL); // 子进程结束。默认忽略
signal(SIGSEGV, uwsgi_segfault); // Invalid memory reference/Segmentation Fault
uwsgi_log("!!! uWSGI process %d got Segmentation Fault !!!\n", (int) getpid());
signal(signum, SIG_DFL);
signal(SIGFPE, uwsgi_fpe); // Floating-point exception
uwsgi_log("!!! uWSGI process %d got Floating Point Exception !!!\n", (int) getpid());
kill(getpid(), signum);
signal(SIGHUP, SIG_IGN); // Hangup detected on controlling terminal or death of controlling process
signal(SIGTERM, SIG_IGN); // Termination signal
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); // Broken pipe: write to pipe with no readers
masterpid = getpid();
uwsgi_proto_hooks_setup
// 配置一些http协议的处理函数
getcwd
uwsgi_setup_schemes
// ...
uwsgi_register_clock
uwsgi_set_clock
// 注册进程结束时的回调
// fallback config
atexit(uwsgi_fallback_config);
// 貌似一个用一个备用的配置再次启动
// manage/flush logs
atexit(uwsgi_flush_logs);
// 貌似尝试读完pipe
// clear sockets, pidfiles// ...
atexit(vacuum);
// 各种清理/unlink
// call user scripts
atexit(uwsgi_exec_atexit);
// 自定义回调
// 创建进程间共享内存
uwsgi.shared = (struct uwsgi_shared *) uwsgi_calloc_shared(sizeof(struct uwsgi_shared));
uwsgi_malloc_shared
void *addr = mmap(NULL, size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANON, -1, 0);
// mmap创建共享内存。须重点学习
// plugin初始化为空
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
uwsgi.p[i] = &unconfigured_plugin;
}
uwsgi_init_default
// 设置大量默认参数
uwsgi_check_emperor // 帝王模式。可忽略
uwsgi_setup_reload
uwsgi_register_base_hooks
// 注册各种基本操作
uwsgi_register_logchunks
// ???
uwsgi_log_encoders_register_embedded
uwsgi_metrics_collectors_setup
UWSGI_LOAD_EMBEDDED_PLUGINS
build_options
// uwsgi_base_options是写死的选项
// 把这些选项和custom选项整理放到uwsgi.options
parse_sys_envs(UWSGI_ENVIRON);
uwsgi_commandline_config
// 对整理好的选项,用getopt_long解析命令行参数。
add_exported_option(optname, optarg, 0);
// 添加
uwsgi_configure
// 看情况对每个选项调用对应的uwsgi_option.func
// 执行一些需要先执行的流程比如exec_asap
// logto参数设置uwsgi.logfile
// 可做daemonize
//
uwsgi_setup_log
daemonize
logto
logto
// 可选log打到文件或udp socket
// setup offload engines
uwsgi_offload_engines_register_all();
// setup main loops
// worker的loop。重点。后续详细看流程
uwsgi_register_loop("simple", simple_loop);
uwsgi_register_loop("async", async_loop);
// setup cheaper algos
// cheaper机制。需要研究
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Cheaper.html
uwsgi_register_cheaper_algo("spare", uwsgi_cheaper_algo_spare);
uwsgi_register_cheaper_algo("backlog", uwsgi_cheaper_algo_backlog);
uwsgi_register_cheaper_algo("manual", uwsgi_cheaper_algo_manual);
// setup imperial monitors
uwsgi_register_imperial_monitor("dir", uwsgi_imperial_monitor_directory_init, uwsgi_imperial_monitor_directory);
uwsgi_register_imperial_monitor("glob", uwsgi_imperial_monitor_glob_init, uwsgi_imperial_monitor_glob);
// setup stats pushers
// 状态推送
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/PushingStats.html
uwsgi_stats_pusher_setup();
// register embedded alarms
uwsgi_register_embedded_alarms();
// 可选择列出各种配置
show_config
plugins_list
loggers_list
cheaper_algo_list
router_list
loop_list
imperial_monitor_list
clocks_list
alarms_list
// 打印各种重要信息
uwsgi_log_initial("*** Starting uWSGI %s (%dbit) on [%.*s] ***\n", UWSGI_VERSION, (int) (sizeof(void *)) * 8, 24, ctime((const time_t *) &uwsgi.start_tv.tv_sec));
// 初始化shared_sockets
// shared-socket选项
uwsgi_setup_shared_sockets
uwsgi_emperor_start // 帝王模式。忽略
// jail系统
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Namespaces.html
uwsgi_start
uwsgi_set_cgroup // cgroup参数。忽略
// jail相关。namespace相关参数。忽略
// ...
uwsgi_log_initial("your memory page size is %d bytes\n", uwsgi.page_size);
uwsgi_setup_locking
// 配置uwsgi.lock_ops相关的操作
// 宏走的 #define UWSGI_LOCK_ENGINE_NAME "pthread robust mutexes"
// 惊群问题Thundering Herd
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/articles/SerializingAccept.html
uwsgi_rpc_init
// uwsgi_calloc_shared创建rpc_table等共享数据
// 初始化所有uwsgi.sharedareas。忽略
uwsgi_sharedareas_init
uwsgi_sharedarea_init
// queue框架
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Queue.html
uwsgi_init_queue // 没用到
// caching框架
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Caching.html
uwsgi_cache_create_all // 没用到
uwsgi_alarms_init
// exception-handler选项
uwsgi_exception_setup_handlers
// 注册uwsgi/http等协议处理
uwsgi_protocols_register
uwsgi_register_protocol("uwsgi", uwsgi_proto_uwsgi_setup);
// gp的init
// no-server选项
uwsgi_setup_systemd();
uwsgi_setup_upstart();
uwsgi_setup_zerg();
uwsgi_setup_emperor();
uwsgi_setup_inherited_sockets
// 上面的一些操作可能会创建socket初始数据,放入uwsgi.sockets。
// 配置中的socket参数指定了主接收socket。也已经创建。
uwsgi_bind_sockets
// 进行实际的socket创建
// 对每个socket
if (tcp_port == NULL) {
uwsgi_sock->fd = bind_to_unix(uwsgi_sock->name, uwsgi.listen_queue, uwsgi.chmod_socket, uwsgi.abstract_socket);
// 分配sockaddr_un内存
serverfd = create_server_socket(AF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM);
// 创建socket
// https://linux.die.net/man/2/socket
int serverfd = socket(domain, type, 0);
// setsockopt各种设置
// https://linux.die.net/man/2/bind
bind(serverfd, (struct sockaddr *) uws_addr, len + ((void *) uws_addr->sun_path - (void *) uws_addr))
// https://linux.die.net/man/2/listen
// uwsgi的listen参数是直接传到listen接口
listen(serverfd, listen_queue)
} else {
uwsgi_sock->fd = bind_to_tcp(uwsgi_sock->name, uwsgi.listen_queue, tcp_port);
socket_to_in_addr(socket_name, tcp_port, 0, (struct sockaddr_in *) &uws_addr);
uwsgi_resolve_ip
gethostbyname
inet_ntoa
serverfd = create_server_socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM);
// 根据配置进行各种setsockopt
bind(serverfd, (struct sockaddr *) &uws_addr, addr_len)
listen(serverfd, listen_queue)
}
uwsgi_set_sockets_protocols
// uwsgi_protocols_register中注册了各种协议
// 这里调用注册的setup函数
uwsgi_socket_setup_protocol
uwsgi_proto_uwsgi_setup
// 设置socket的各种基本操作函数。例如accept等等,对这些c库的socket操作进行封装。
// p plugin初始化
// plugin的post_init
// uwsgi.has_threads相关处理
pthread_mutex_init
// cron相关
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Cron.html
uwsgi_setup_workers
// numproc是processes或workers参数配置的
// 每个worker都会起进程
// 这里给uwsgi.workers起各种数据
// 用uwsgi_calloc_shared分配共享内存
// 那么master和各个worker(各进程间)就能读写同一份数据了
uwsgi.workers = (struct uwsgi_worker *) uwsgi_calloc_shared(sizeof(struct uwsgi_worker) * (uwsgi.numproc + 1));
for (i = 0; i <= uwsgi.numproc; i++) {
// allocate memory for apps
uwsgi.workers[i].apps = (struct uwsgi_app *) uwsgi_calloc_shared(sizeof(struct uwsgi_app) * uwsgi.max_apps);
// allocate memory for cores
uwsgi.workers[i].cores = (struct uwsgi_core *) uwsgi_calloc_shared(sizeof(struct uwsgi_core) * uwsgi.cores);
}
create_signal_pipe
uwsgi_setup_mules_and_farms
uwsgi_log("*** Operational MODE: preforking+async ***\n");
uwsgi_setup_metrics
// uwsgi.logformat
// spoolers
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Spooler.html
// plugin的preinit_apps
// lazy和lazy-apps参数
if (!uwsgi.lazy && !uwsgi.lazy_apps) {
uwsgi_init_all_apps();
// exec-pre-app参数
uwsgi_run_command_and_wait
fork
// 父进程
waitpid
// 子进程
uwsgi_run_command_do
execvp
// call-pre-app参数
uwsgi_call_symbol
dlsym
func
// plugin的init_apps()
uwsgi_python_init_apps
// 见下面python plugin流程
// mount参数
每个uwsgi.mounts
每个uwsgi.p
if (uwsgi.p[j]->mount_app)
uwsgi_log("mounting %s on %s\n", what, app_mps->value);
mount_app
uwsgi_python_mount_app
// 见下面的python plugin流程
// exec-post-app参数
// call-post-app参数
uwsgi_call_symbol
}
atexit(uwsgi_plugins_atexit);
// plugin的atexit()
// plugin的postinit_apps
// uwsgi.daemonize2
// 检查plugin是否已经配置
uwsgi_alarm_thread_start();
uwsgi_exceptions_handler_thread_start();
// plugin的master_fixup
spooler_start
uwsgi_notify_ready
// 生成worker。workers参数或processes参数。
uwsgi_respawn_worker(int wid)
// 设置uwsgi.workers[wid]的各种数据
// plugin的pre_uwsgi_fork
uwsgi_fork
if(master) // 父进程
plugin的post_uwsgi_fork
uwsgi.workers[wid].pid = pid; // 记录worker的pid
elif(worker) // 子进程
// plugin的post_uwsgi_fork
signal(SIGWINCH, worker_wakeup);
signal(SIGTSTP, worker_wakeup);
// 设置/初始化worker的各种数据
uwsgi.mywid = wid;
uwsgi.mypid = getpid();
uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].id = uwsgi.mywid;
// ...
uwsgi_fixup_fds
// plugin的master_fixup
uwsgi_run
master_loop // (用masterpid确定)
uwsgi_init_rb_timer // 初始化timer的红黑树
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGTSTP, suspend_resume_them_all);
suspend_resume_them_all
// toggle所有worker的suppend状态?
// subscribe系列参数
uwsgi_subscribe_all(suspend, 1);
// 给每个worker发SIGTSTP
kill(uwsgi.workers[i].pid, SIGTSTP)
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGHUP, grace_them_all);
grace_them_all
uwsgi.status.gracefully_reloading = 1;
uwsgi_destroy_processes
uwsgi_detach_daemons
对uwsgi.daemons中的所有
// https://www.man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/kill.2.html
// 检测不正常的daemon。signal发0。
kill(ud->pid, 0)
// 如果做相应处理
// 发SIGKILL等等
// kill所有gateway
kill(ushared->gateways[i].pid, SIGKILL);
uwsgi_log("// ...gracefully killing workers// ...\n");
// 每个worker走uwsgi_curse(i, SIGHUP);
// 每个mule走uwsgi_curse_mule(i, SIGHUP);
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGTERM, reap_them_all);
uwsgi_destroy_processes
// 每个worker走uwsgi_curse(i, SIGTERM);
// 每个mule走uwsgi_curse_mule(i, SIGTERM);
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGQUIT, kill_them_all);
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGINT, kill_them_all);
kill_them_all
uwsgi.status.brutally_destroying = 1;
// 每个worker走uwsgi_curse(i, SIGINT);
// 每个mule走uwsgi_curse_mule(i, SIGINT);
uwsgi_destroy_processes
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGUSR1, stats);
stats
// 打印config和worker信息
atexit(uwsgi_master_cleanup_hooks);
uwsgi_master_cleanup_hooks
// 所有plugin调master_cleanup
uwsgi.master_queue = event_queue_init();
epfd = epoll_create(256);
event_queue_add_fd_read // 监听各种fd
epoll_ctl(eq, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &ee)
uwsgi_metrics_start_collector
pthread_create
uwsgi_metrics_loop
for(;;) {
// 收集metrics信息
sleep(1);
}
uwsgi_add_reload_fds
uwsgi_cache_start_sweepers
uwsgi_cache_start_sync_servers
// 各种功能初始化
// zerg_server初始化
// stats服务初始化
// stats参数和stats-http参数配置
uwsgi.stats_fd = bind_to_tcp(uwsgi.stats, uwsgi.listen_queue, tcp_port);
event_queue_add_fd_read(uwsgi.master_queue, uwsgi.stats_fd);
uwsgi_log("*** Stats server enabled on %s fd: %d ***\n", uwsgi.stats, uwsgi.stats_fd);
// uwsgi.stats_pusher_instances
// uwsgi.udp_socket
// udp服务器
uwsgi_setup_snmp
// uwsgi.status.is_cheap
uwsgi_mule // 初始化mule
uwsgi_fork
// 子进程
uwsgi_close_all_sockets
uwsgi_mule_run
uwsgi_mule_handler
for (;;) {
}
gateway_respawn
uwsgi_fork
// 子进程
ug->loop(id, ug->data);
// attach-daemon参数配置另外的daemon程序。在此启动
uwsgi_daemons_spawn_all
uwsgi_spawn_daemon
uwsgi_fork
// 子进程
daemon_spawn
uwsgi_exec_command_with_args
execvp
uwsgi_cache_sync_all
msync
// 处理各种touch
uwsgi_check_touches(uwsgi.touch_reload);
stat
// fs monitor
uwsgi_fsmon_setup
// uwsgi.requested_cheaper_algo
// master主循环
for (;;) {
uwsgi_master_check_death
uwsgi_master_check_reload
uwsgi_master_check_chain
uwsgi_master_check_mercy
uwsgi_daemons_smart_check
// https://linux.die.net/man/2/waitpid
// 等待某个子进程状态发生变化
diedpid = waitpid(WAIT_ANY, &waitpid_status, WNOHANG);
if (diedpid == -1) {
// 出错
}
if (diedpid == 0) { // 无改变。执行master的日常工作。
// 处理ushared->files_monitored
// 如果没注册进行注册
// 处理ushared->timers的注册
// 处理ushared->rb_timers的注册
// 检测ushared->rb_timers的超时
uwsgi_route_signal // 超时发送signal
uwsgi_signal_send // 往各种signal_pipe发
// 等一个事件。比如
rlen = event_queue_wait(uwsgi.master_queue, check_interval, &interesting_fd);
epoll_wait
uwsgi_update_load_counters
uwsgi_manage_signal_cron
// cron参数。可配置cron
uwsgi_manage_command_cron
uwsgi_cron_task_needs_execution
// 检查时间
uwsgi_run_command
fork
execvp
// 如果有事件,处理事件。
if (rlen > 0) {
// if the following function returns -1, a new worker has just spawned
if (uwsgi_master_manage_events(interesting_fd)) {
// 处理各种事件
// 比如我们配置了stats参数,从外部用http查询状态。会走uwsgi_send_stats传回状态。
return 0;
}
}
// logrotate操作
// logto参数设置
uwsgi_check_logrotate
uwsgi_master_check_idle
// idle参数和die-on-idle参数
// 检查idle状态。做一些操作。可能设为cheap mode。
master_check_listen_queue
// 检查socket状态
// getsockopt得到queue和max_queue
// 如果queue满了。打印。
// 这个出现在大量请求处理不过来的场景。
if (uwsgi_sock->queue > 0 && uwsgi_sock->queue >= uwsgi_sock->max_queue) {
uwsgi_log_verbose("*** uWSGI listen queue of socket \"%s\" (fd: %d) full !!! (%llu/%llu) ***\n", uwsgi_sock->name, uwsgi_sock->fd, (unsigned long long) uwsgi_sock->queue, (unsigned long long) uwsgi_sock->max_queue);
}
// check各种deadline
uwsgi_master_check_workers_deadline
// 各种原因导致需要杀死之类的操作。执行
// check-mountpoint参数。如果mountpoint不存在了。
uwsgi_master_check_mountpoints
uwsgi_check_mountpoint
statfs // 检查文件。如果不存在,uwsgi_nuclear_blast全完蛋。
// resubscribe every 10 cycles by default
uwsgi_subscribe_all
uwsgi_cache_sync_all
// https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/msync.2.html
// 同步mmap共享数据
msync // synchronize a file with a memory map。
// 检查touch_reload
if (!uwsgi_instance_is_reloading && !uwsgi_instance_is_dying) {
char *touched = uwsgi_check_touches(uwsgi.touch_reload);
// 通过时间戳等手段检查是否touch
if (touched) {
uwsgi_log_verbose("*** %s has been touched// ... grace them all !!! ***\n", touched);
uwsgi_block_signal(SIGHUP);
grace_them_all(0);
uwsgi_unblock_signal(SIGHUP);
continue;
}
}
// 如果没有child状态改变,直接continue。
continue
}
// 有child状态改变
uwsgi_deadlock_check(diedpid); // lock相关暂未研究
// check各种death
uwsgi_master_check_daemons_death(diedpid)
uwsgi_master_check_cron_death(diedpid
// ...
int thewid = find_worker_id(diedpid);
if (thewid <= 0) { // 不是worker。基本只是uwsgi_log一下?
// 检查是否uwsgi.spoolers
// 检查是否uwsgi.mules
// 检查是否ushared->gateways
if (uwsgi_daemon_check_pid_death(diedpid))
continue
continue
}
// 是worker进程结束
uwsgi.workers[thewid].pid = 0;
if (WIFEXITED(waitpid_status) && WEXITSTATUS(waitpid_status) == UWSGI_FAILED_APP_CODE) {
if (uwsgi.lazy_apps && uwsgi.need_app) {
kill_them_all
}
}
// 处理各种waitpid_status
// 准备重新生成worker
// avoid fork bombing
// 如发现check_interval间隔内过于频繁地重启worker,会sleep一会。
// 见forkbomb-delay参数和check-interval参数
uwsgi_respawn_worker
// 见之前的分析
}
worker#
main
uwsgi_setup
流程见上面的master
uwsgi_run
此时进程身份是worker
// eventually maps (or disable) sockets for the worker
// map-socket参数。忽略。
uwsgi_map_sockets();
// worker-exec参数
if (uwsgi.worker_exec) {
execvp
exit(1);
}
// offload-threads参数
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/OffloadSubsystem.html
if (uwsgi.offload_threads > 0) {
uwsgi_offload_thread_start
uwsgi_thread_new(uwsgi_offload_loop)
for (;;) {
event_queue_wait_multi
event_func
}
}
// plugin的post_fork
// worker-exec2参数
if (uwsgi.worker_exec2) {
execvp
exit(1);
}
// plugin的worker()。只有python的plugin用到。
uwsgi_python_worker
// 见下面的plugin流程。实际没什么用
uwsgi_worker_run
// lazy和lazy-apps参数
if (uwsgi.lazy || uwsgi.lazy_apps) {
uwsgi_init_all_apps();
// 见master
}
// 初始化请求的承载资源
// async_queue_unused里的每个wsgi_request对应一个http请求。
// 如果用尽,就不接受新的请求。
if (uwsgi.async > 1) { // gevent参数设置为256
// a stack of unused cores
uwsgi.async_queue_unused = uwsgi_malloc(sizeof(struct wsgi_request *) * uwsgi.async);
// fill it with default values
for (i = 0; i < uwsgi.async; i++) {
uwsgi.async_queue_unused[i] = &uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].cores[i].req;
}
// the first available core is the last one
uwsgi.async_queue_unused_ptr = uwsgi.async - 1;
}
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGHUP, gracefully_kill);
// master通知worker正常停止。发SIGHUP
gracefully_kill
uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].manage_next_request = 0;
if (uwsgi.threads > 1) { // 这里应该是不走
wait_for_threads
pthread_mutex_lock(&uwsgi.six_feet_under_lock); // 争锁
遍历uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].cores
确认自己的thread_id存在
pthread_cancel(thread_id) // 尝试cancel线程。
pthread_join(thread_id) // join
}
if (uwsgi.async > 1) {
if (uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].shutdown_sockets)
uwsgi_shutdown_all_sockets();
对于所有uwsgi.sockets
shutdown
close
exit(UWSGI_RELOAD_CODE);
}
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGINT, end_me);
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGTERM, end_me);
end_me
exit // 直接exit
uwsgi_unix_signal(SIGUSR1, stats);
stats
打印信息
signal(SIGUSR2, (void *) &what_i_am_doing);
what_i_am_doing
打印信息
// 所有plugin->fixup
uwsgi.chdir2
// 清空req
// async_id按index设置
for (i = 0; i < uwsgi.cores; i++) {
memset(&uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].cores[i].req, 0, sizeof(struct wsgi_request));
uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].cores[i].req.async_id = i;
}
// 每个worker的cores[0]的thread_id,设为当前的thread_id。
if (uwsgi.cores > 1) {
uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].cores[0].thread_id = pthread_self();
pthread_mutex_init(&uwsgi.six_feet_under_lock, NULL);
}
uwsgi_ignition
// plugin的hijack_worker
uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].accepting = 1;
// 执行一些hook
uwsgi_hooks_run(uwsgi.hook_accepting, "accepting", 1);
// 三种loop
// 主要看gevent的loop
if (uwsgi.loop) {
void (*u_loop) (void) = uwsgi_get_loop(uwsgi.loop);
// 运行plugin的loop比如gevent/asyncio
u_loop
gevent_loop
// 见下方流程
} else {
// 其他loop。未详细看,可能有错。
if (uwsgi.async < 2) {
simple_loop(); // 简单loop
uwsgi_loop_cores_run(simple_loop_run);
pthread_create启动线程
simple_loop_run
event_queue_init
// 根据选择(epoll/kqueue/poll)初始化event_queue
uwsgi_add_sockets_to_queue(main_queue, core_id);
// 相关的socket进queue。比如epoll开始监听。
// 死循环监听事件/接收数据/处理请求
while (uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].manage_next_request) {
wsgi_req_setup
// 准备一个新的wsgi请求
wsgi_req_accept // 等待新链接
thunder_lock
event_queue_wait
epoll_wait
proto_accept
uwsgi_proto_base_accept
accept
wsgi_req_recv // 等待对端数据
proto
uwsgi_proto_uwsgi_parser
read
uwsgi_wait_read_req
wait_read_hook
uwsgi_simple_wait_read_hook
uwsgi.p[wsgi_req->uh->modifier1]->request(wsgi_req);
// wsgi协议处理
uwsgi_request_wsgi
init_uwsgi_app
wsgi_env_create
request_subhandler
uwsgi_request_subhandler_wsgi
python_call
PyObject_CallObject
uwsgi_close_request
}
}
else {
async_loop(); // 异步loop
uwsgi_async_init
event_queue_init
uwsgi_add_sockets_to_queue
// 死循环监听事件/接收数据/处理请求
while (uwsgi.workers[uwsgi.mywid].manage_next_request) {
event_queue_wait_multi // 等待事件
for(所有事件){
if(is_a_new_connection){
wsgi_req_setup
wsgi_req_simple_accept
proto_accept
wsgi_req_async_recv
}
if(!is_a_new_connection){
proto
uwsgi_proto_uwsgi_parser
read
runqueue_push // 插入可能的req
}
}
// 协程处理堆积的req
}
}
}
// 正常一直在上面的loop中运行。走不到这。
python plugin#
// 在uwsgi中嵌入python,执行python代码。
// https://docs.python.org/3/extending/embedding.html
init
uwsgi_python_init
// 在c环境中起python环境
// 然后可用python的c接口对python环境进行各种操作,执行外部python代码等等。
Py_GetVersion
Py_GetCompiler
// 检已初始化。获取gil。
if (Py_IsInitialized()) {
uwsgi_log("--- Python VM already initialized ---\n");
PyGILState_Ensure();
goto ready;
}
Py_SetProgramName // 没完全懂
Py_Initialize
preinit_apps
uwsgi_python_preinit_apps
init_pyargv
PySys_SetArgv(up.argc, up.py_argv);
PyDict_SetItemString(sys_dict, "executable", PyUnicode_FromString(up.executable));
init_uwsgi_embedded_module
// 主要初始化python的uwsgi module环境。
// 这样后续运行的外部python文件也也已调用uwsgi的各种函数。
// https://docs.python.org/3/c-api/typeobj.html
// https://docs.python.org/3/c-api/allocation.html#c.PyObject_New
// 初始化uwsgi_InputType配置。相当于创建一个新python类型uwsgi._Input。
// 在uwsgi_request_subhandler_wsgi里会PyObject_New创建实例。
// 实际的数据包含struct wsgi_request。基本包含了一个请求的各种数据。
PyType_Ready(&uwsgi_InputType)
// 做一个workers的tuple。每个存一个dict。
up.workers_tuple = PyTuple_New(uwsgi.numproc);
for (i = 0; i < uwsgi.numproc; i++) {
zero = PyDict_New();
Py_INCREF(zero);
PyTuple_SetItem(up.workers_tuple, i, zero);
}
// 创建uwsgi module
PyImport_AppendInittab("uwsgi", init_uwsgi3);
init_uwsgi3
PyModule_Create
// 获取uwsgi
new_uwsgi_module = PyImport_AddModule("uwsgi");
// 获取uwsgi.__dict__
up.embedded_dict = PyModule_GetDict(new_uwsgi_module);
// 对up.embedded_dict操作。往module里加各种参数/函数
// 处理与python plugin相关的配置参数。比如module和callable。参数添加到up.embedded_dict的opt
// uwsgi.sockets里的sockets添加到sockets
// magic_table等等
init_uwsgi_module_advanced
// 添加uwsgi_advanced_methods和uwsgi_metrics_methods
// 包含较多辅助功能。比如查询worker状态等
init_uwsgi_module_cache
// 添加uwsgi_cache_methods
// https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Queue.html
if (uwsgi.queue_size > 0) {
init_uwsgi_module_queue(new_uwsgi_module);
}
uwsgi_init_symbol_import
PyImport_ImportModule("uwsgi");
// 继续初始化一些类型,放到uwsgi模块。
init_uwsgi_vars
// 配置一些环境。path之类。不纠结
init_apps
// 初始化app,即Flask项目
uwsgi_python_init_apps
// 初始化up.loaders
// 我们配置中的module参数设置了up.wsgi_config。走uwsgi_uwsgi_loader
if (up.wsgi_config != NULL) {
init_uwsgi_app(LOADER_UWSGI, up.wsgi_config, uwsgi.wsgi_req, up.main_thread, PYTHON_APP_TYPE_WSGI);
// 这个函数新增一个app。可有多个app。
// 新增id
int id = uwsgi_apps_cnt;
wi = &uwsgi_apps[id];
// 按配置拿到flask项目的main.py里的main_app
wi->callable = up.loaders[loader](arg1);
uwsgi_uwsgi_loader(arg1)
quick_callable = up.callable; // 设置为main_app
// arg1为配置中的module=main。此时需要存在一个main.py作为入口module。
wsgi_dict = get_uwsgi_pydict(module);
wsgi_module = PyImport_ImportModule(module);
// 此时import了main.py。就已经实际运行了main.py。
// 我的main.py里触发一系列初始化动作,有打印log。此时可以看到log。
// 按wsgi协议,flask需要返回一个callable给uwsgi调用。
// main.py里最终要有个类似main_app = Flask("myapp")的流程。即用flask接口生成一个callable。
// 拿到main.py的__dict__
wsgi_dict = PyModule_GetDict(wsgi_module);
// 返回main.py里的main_app
return PyDict_GetItemString(wsgi_dict, quick_callable);
if (PyDict_Check((PyObject *)wi->callable)) {
// callable为dict。多个app。暂时忽略。
}
// 起uwsgi.cores个environ
wi->environ = malloc(sizeof(PyObject*)*uwsgi.cores);
if (!wi->environ) {
uwsgi_error("malloc()");
exit(1);
}
// 每个cores起dict
// environ后续存放一个请求的参数和一些环境数据
for(i=0;i<uwsgi.cores;i++) {
wi->environ[i] = PyDict_New();
if (!wi->environ[i]) {
uwsgi_log("unable to allocate new env dictionary for app\n");
exit(1);
}
}
if (app_type == PYTHON_APP_TYPE_WSGI) {
wi->request_subhandler = uwsgi_request_subhandler_wsgi;
wi->response_subhandler = uwsgi_response_subhandler_wsgi;
wi->argc = 2;
}
// 起uwsgi.cores个wi->args
// 每个arg设置为(0, wsgi_spitout)
// 处理请求时会把0设置为wsgi_req->async_environ。最后传给flask流程。
if (app_type == PYTHON_APP_TYPE_WSGI) {
// prepare sendfile() for WSGI app
wi->sendfile = PyCFunction_New(uwsgi_sendfile_method, NULL);
wi->eventfd_read = PyCFunction_New(uwsgi_eventfd_read_method, NULL);
wi->eventfd_write = PyCFunction_New(uwsgi_eventfd_write_method, NULL);
}
// 设置wi->gateway_version
// 设置wi->uwsgi_version
// wi->uwsgi_node
// 打印
if (app_type == PYTHON_APP_TYPE_WSGI) {
uwsgi_log( "WSGI app %d (mountpoint='%.*s') ready in %d seconds on interpreter %p pid: %d%s\n", id, wi->mountpoint_len, wi->mountpoint, (int) wi->startup_time, wi->interpreter, (int) getpid(), default_app);
}
// emulate COW
// copy on write?
uwsgi_emulate_cow_for_apps(id);
}
mount_app
// 和uwsgi_python_init_apps基本一个意思。加载app。
uwsgi_python_mount_app(char *mountpoint, char *app)
// 配置中 mount = /api/=main.py
// 那么app=main.py。mountpoint=/api/
// 设置uwsgi.wsgi_req的一些数据
id = init_uwsgi_app(LOADER_MOUNT, app, uwsgi.wsgi_req, up.main_thread, PYTHON_APP_TYPE_WSGI);
// 和上面的LOADER_UWSGI大同小异。主要是loader的区别
uwsgi_mount_loader
callable = uwsgi_file_loader((void *)what);
wsgi_file_module = uwsgi_pyimport_by_filename(py_filename, filename);
// 读py文件
// parse and compile
py_compiled_node = Py_CompileString(pycontent, real_filename, Py_file_input);
// 运行。返回module。
py_file_module = PyImport_ExecCodeModule(name, py_compiled_node);
return py_file_module;
wsgi_file_dict = PyModule_GetDict(wsgi_file_module);
wsgi_file_callable = PyDict_GetItemString(wsgi_file_dict, callable);
return wsgi_file_callable;
worker
uwsgi_python_worker()
// 一般忽略
if (!up.worker_override)
return 0;
配置中同时配置了module和mount。其实是错的,这样实际会起2个uwsgi的app,走同一个flask项目。
可把module参数去掉。
多个app的例子?
https://uwsgi-docs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Snippets.html#multiple-flask-apps-in-different-mountpoints
gevent plugin#
// worker最后走gevent_loop
gevent_loop
PyObject *gevent_dict = get_uwsgi_pydict("gevent"); // import gevent
PyImport_ImportModule
PyModule_GetDict
// 检查version
if (ugevent.monkey) {
monkey_patch();
}
// PyDict_GetItemString
// PyCFunction_New
// 获取和定义各种功能
ugevent.spawn = PyDict_GetItemString(gevent_dict, "spawn");
// 直接用sleep触发切换,把自己切换出去。
ugevent.greenlet_switch = PyDict_GetItemString(gevent_dict, "sleep");
if (!ugevent.greenlet_switch) uwsgi_pyexit;
PyObject *gevent_get_hub = PyDict_GetItemString(gevent_dict, "get_hub");
ugevent.hub = python_call(gevent_get_hub, PyTuple_New(0), 0, NULL);
// https://www.gevent.org/api/gevent.hub.html#gevent.hub.get_hub
// ugevent.hub是默认打头的协程,相当于根协程,在它基础上不断派生新的协程。
// 可作为调度者
// 当请求处理的协程需要等待io而切换时,就切换回ugevent.hub。
// https://www.gevent.org/api/gevent.hub.html#the-event-loop
ugevent.hub_loop = PyObject_GetAttrString(ugevent.hub, "loop");
PyObject *uwsgi_gevent_main = PyCFunction_New(uwsgi_gevent_main_def, NULL);
// ...
// greenlet to run at each request
// 设置greenlet的处理函数。处理一个http请求。
PyObject *uwsgi_request_greenlet = PyCFunction_New(uwsgi_gevent_request_def, NULL);
// 设置第一个参数为处理函数
ugevent.greenlet_args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(ugevent.greenlet_args, 0, uwsgi_request_greenlet);
py_uwsgi_gevent_request
// 初始化watcher
ugevent.watchers = uwsgi_malloc(sizeof(PyObject *) * uwsgi_count_sockets(uwsgi.sockets));
while(uwsgi_sock) {
// https://www.gevent.org/api/gevent.hub.html#gevent._interfaces.ILoop.io
// 调用gevent的hub_loop的io函数。创建watcher。
// PyObject_CallMethod的参数说明见https://docs.python.org/3/c-api/arg.html
ugevent.watchers[i] = PyObject_CallMethod(ugevent.hub_loop, "io", "ii", uwsgi_sock->fd, 1);
// start启动watcher
// https://www.gevent.org/api/gevent.hub.html#gevent._interfaces.IWatcher
PyObject_CallMethod(ugevent.watchers[i], "start", "Ol", uwsgi_gevent_main, (long)uwsgi_sock);
// 这里设置了watcher的回调。如果有客户端连上服务器,socket可accept,就走uwsgi_gevent_main。
py_uwsgi_gevent_main
// 申请一个wsgi_req资源
wsgi_req = find_first_available_wsgi_req();
// 取uwsgi.async_queue_unused中最后一个
// async_queue_unused是看作资源队列而不是任务队列
wsgi_req_setup(wsgi_req, wsgi_req->async_id, uwsgi_sock);
// 给wsgi_req填各种数据
// async_id是资源的index编号,定死的。
// 这个请求就绑定在async_id了。
// 也就绑定在当前worker的cores[async_id]这个core了。
// 设置core的in_request=1
// 实际accept新的socket
wsgi_req_simple_accept(wsgi_req, uwsgi_sock->fd)
wsgi_req->fd = wsgi_req->socket->proto_accept(wsgi_req, fd);
uwsgi_proto_base_accept
accept
// 设置第二个参数
PyTuple_SetItem(ugevent.greenlet_args, 1, PyLong_FromLong((long)wsgi_req));
// spawn协程。传入greenlet_args
PyObject *new_gl = python_call(ugevent.spawn, ugevent.greenlet_args, 0, NULL);
py_uwsgi_gevent_request
// 取出wsgi_req
PyObject *py_wsgi_req = PyTuple_GetItem(args, 0);
// 到此wsgi_req只是做了初始化,分配资源等。
// 不断读socket。并尝试解析请求。
for(;;) {
int ret = uwsgi.wait_read_hook(wsgi_req->fd, uwsgi.socket_timeout);
// 准备读。等到真的可读或者超时时,切回来处理。
// 有异常的话跳出循环
uwsgi_gevent_wait_read_hook
// 给wsgi_req->fd创建io watcher监听io数据
PyObject *watcher = PyObject_CallMethod(ugevent.hub_loop, "io", "ii", fd, 1);
// 创建time watcher监听超时
PyObject *timer = PyObject_CallMethod(ugevent.hub_loop, "timer", "i", timeout);
PyObject *current_greenlet = GET_CURRENT_GREENLET;
PyObject *current = PyObject_GetAttrString(current_greenlet, "switch");
// 启动watcher。
// 回调操作为current_greenlet.switch。
// 即切换到current_greenlet也就是切换回此协程进行下一步操作。
ret = PyObject_CallMethod(watcher, "start", "OO", current, watcher);
// 同样启动timer
ret = PyObject_CallMethod(timer, "start", "OO", current, timer);
// 此时切换回hub。当socket有数据或者timer超时时切回来。
ret = PyObject_CallMethod(ugevent.hub, "switch", NULL);
// 回到此地。清理watcher
stop_the_watchers_and_clear
// 走到这说明socket有数据或超时。
// 尝试初步解析。根据数据长度判断是否为合法的wsgi请求。
// 如果有错跳出循环
// 如果数据不全继续循环读
// 如果成功解析,跳出并处理请求。
int status = wsgi_req->socket->proto(wsgi_req);
uwsgi_proto_uwsgi_setup里设置了uwsgi_sock->proto = uwsgi_proto_uwsgi_parser;
// 解析wsgi请求
uwsgi_proto_uwsgi_parser
// 读socket
read(wsgi_req->fd, ptr + wsgi_req->proto_parser_pos, (uwsgi.buffer_size + 4) - wsgi_req->proto_parser_pos);
// 判断长度
}
// 如果是一个合法的请求
for(;;) {
// plugin的request
if (uwsgi.p[wsgi_req->uh->modifier1]->request(wsgi_req) <= UWSGI_OK) {
// python plugin的request
uwsgi_request_wsgi
uwsgi_parse_vars(wsgi_req)
// 相当多的具体数据解析。不细看了。
wsgi_req->async_environ = up.wsgi_env_create(wsgi_req, wi);
// 处理请求
request_subhandler
uwsgi_request_subhandler_wsgi
// 各种数据填到wsgi_req->async_environ
// 最后放到wsgi_req->async_args
// 涉及wsgi协议
wsgi_req->async_app = wi->callable;
// 最后调用callable。也就是配置里的main_app。
// 到此请求就转到flask项目了。
return python_call(wsgi_req->async_app, wsgi_req->async_args, uwsgi.catch_exceptions, wsgi_req);
PyObject_CallObject
// 返回请求
response_subhandler
uwsgi_response_subhandler_wsgi
int ret = uwsgi_python_send_body(wsgi_req, pychunk);
uwsgi_response_write_body_do
// 各种写socket。不细看
// 包括返回文件uwsgi_proto_base_sendfile的情况
// 最后走linux的sendfile()
goto end;
}
wsgi_req->switches++;
// switch after each yield
GEVENT_SWITCH
// 即sleep(0)。切换出去。
}
uwsgi_close_request(wsgi_req);
// 收尾工作
// 设置状态
// close socket
// 各种free
free_req_queue // 释放req资源
// 其他收尾工作
// 到此一个http请求结束了
}
// 一些signal配置
python_call(ugevent.signal, ge_signal_tuple, 0, NULL);
// 体面地结束worker
py_uwsgi_gevent_graceful
// uwsgi_log("Gracefully killing worker %d (pid: %d)// ...\n", uwsgi.mywid, uwsgi.mypid);
// 停止所有watcher
for(i=0;i<count;i++) {
PyObject_CallMethod(ugevent.watchers[i], "stop", NULL);
}
// 等待所有core完成本次请求
// 杀掉主控协程。那么下面对wait_for_me的join就会成功,worker进程就结束了。
PyObject_CallMethod(ugevent.ctrl_gl, "kill", NULL);
// 暴力结束worker
py_uwsgi_gevent_int
// uwsgi_log("Brutally killing worker %d (pid: %d)// ...\n", uwsgi.mywid, uwsgi.mypid);
// 停止所有watcher
for(i=0;i<count;i++) {
PyObject_CallMethod(ugevent.watchers[i], "stop", NULL);
}
// 不等待请求结束。直接杀
PyObject_CallMethod(ugevent.ctrl_gl, "kill", NULL);
// 配置wait_for_me。默认等hub。
PyObject *wait_for_me = ugevent.hub;
// wait_for_hub参数默认关闭
// 改为等ugevent.ctrl_gl
if (!ugevent.wait_for_hub) {
// 起一个控制协程
// 每当子协程切换时
PyObject *uwsgi_greenlet_ctrl_gl_handler = PyCFunction_New(uwsgi_gevent_ctrl_gl_def, NULL);
Py_INCREF(uwsgi_greenlet_ctrl_gl_handler);
PyObject *ctrl_gl_args = PyTuple_New(1);
PyTuple_SetItem(ctrl_gl_args, 0, uwsgi_greenlet_ctrl_gl_handler);
// spawn控制协程。在这里死循环。
// 实际是个dummy。啥也不干。就死循环不断sleep60秒(当然,会切换协程)。
ugevent.ctrl_gl = python_call(ugevent.spawn, ctrl_gl_args, 0, NULL);
py_uwsgi_gevent_ctrl_gl
for(;;) {
// sleep60秒
PyObject_CallObject(ugevent.greenlet_switch, gevent_sleep_args);
}
// 配置为控制协程
wait_for_me = ugevent.ctrl_gl;
}
for(;;) {
// 对wait_for_me = ugevent.ctrl_gl进行join
// 正常情况时join不了的。那么卡在这,除非控制协程结束,意味着worker结束。
// gevent的Greentlet最终继承自greenlet库的greenlet类。
// 它的join调用hub的switch(),最终调用greenlet类的switch,再调run,也就是gevent.Hub的run。
// 最终走libev.ev_run,启动事件循环。
// 这个流程在gevent代码里也看不出来,执行run的流程在greenlet代码里。
if (!PyObject_CallMethod(wait_for_me, "join", NULL)) {
PyErr_Print();
}
else {
break;
}
}
http流程#
// gevent参数
// 指定loop框架为gevent。采用gevent的协程调度。底层事件循环为libev。
// socket参数。服务器的监听socket。客户端或者nginx往这上连。
// 使用default protocol。uwsgi_socket_setup_protocol中会默认设置为uwsgi。
uwsgi_opt_add_socket
uwsgi_new_socket
添加到uwsgi.sockets末尾
// uwsgi_bind_sockets里进行创建/bind/listen
worker的gevent_loop中
// 获取uwsgi.sockets
// 对每个socket的fd创建watcher
watcher绑定py_uwsgi_gevent_main
// mount参数
// mount = /api/=main.py
uwsgi_setup
uwsgi_start
uwsgi_init_all_apps
// 处理参数,找=号,用=号隔开。
mount_app("/api/", "main.py")
uwsgi_python_mount_app
// 加载flask项目,获取flask的app以便后续调用。
// 见上面的plugin流程
// callable 参数
// 上述uwsgi_python_mount_app中指定flask代码中的app名字。
worker起socket并进入事件循环监听
客户端发起或者nginx转发一个新http请求
socket可accept
来到py_uwsgi_gevent_main进行accept
创建一个协程
读socket数据
解析请求
交给flask项目处理
得到flask的结果
结果通过socket发回给客户端或者nginx
请求结束/协程结束